The Enduring Strength of Die Cast Metal Construction: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Enduring Strength of Die Cast Metal Construction: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Strength of Die Cast Metal Construction: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Strength of Die Cast Metal Construction: A Comprehensive Guide

Die casting, a manufacturing process involving the injection of molten metal into a reusable mold, stands as a cornerstone of modern industrial production. This technique, characterized by its efficiency and versatility, yields components with exceptional strength, durability, and intricate detail, making it a preferred choice across numerous industries. This article delves into the intricacies of die cast metal construction, exploring its history, process, advantages, applications, and future prospects.
A Journey Through Time: The Evolution of Die Casting
The roots of die casting can be traced back to the 19th century, with the earliest iterations employing simple hand-operated presses and limited metal choices. However, the advent of the 20th century saw significant advancements, including the development of high-pressure casting machines and the introduction of aluminum and zinc alloys. These innovations dramatically expanded the capabilities and applications of die casting, solidifying its place as a dominant force in manufacturing.
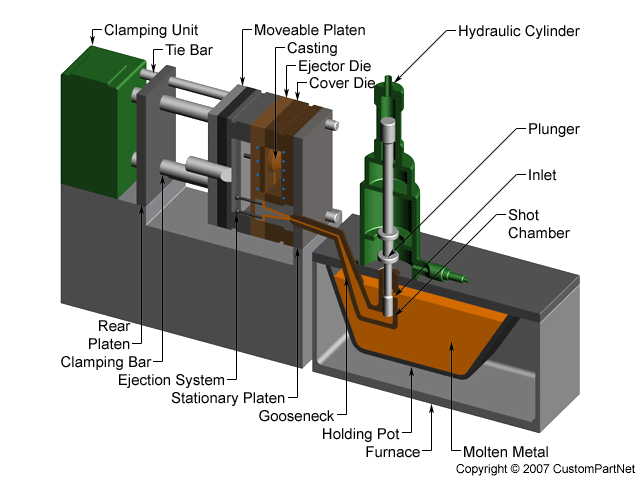
Unveiling the Process: A Step-by-Step Guide to Die Cast Metal Construction
The die casting process, while seemingly straightforward, involves a precise and intricate sequence of steps:
-
Mold Design and Construction: The process begins with the meticulous creation of a mold, known as a die, crafted from hardened steel or other durable materials. The die’s design determines the final shape and dimensions of the cast component.
-
Metal Preparation: The chosen metal, usually an alloy for enhanced properties, is melted in a furnace, ensuring it reaches the correct temperature for fluidity and optimal casting.
-
Injection and Solidification: Once the molten metal is ready, it is injected into the die cavity under high pressure, filling every intricate detail of the mold. The metal rapidly cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the die.
-
Ejection and Finishing: After solidification, the cast component is ejected from the die, usually through a mechanical process. Depending on the application, the component may undergo further finishing steps, including trimming, machining, or surface treatments.
The Power of Precision: Advantages of Die Cast Metal Construction
Die casting offers a multitude of benefits that make it a highly sought-after manufacturing technique:
-
High Production Rates: The use of reusable dies and automated processes enables rapid production of identical components, significantly increasing output compared to other casting methods.
-
Exceptional Detail and Accuracy: The high pressure used in die casting ensures the molten metal fills even the most intricate details of the mold, resulting in components with remarkable precision and dimensional accuracy.
-
Enhanced Strength and Durability: Die cast components exhibit exceptional strength and durability due to the inherent properties of the metals used and the compact, dense structure achieved through the casting process.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: The high production rates and minimal waste generated by die casting contribute to significant cost savings compared to other manufacturing methods, particularly for large-scale production runs.
-
Versatile Applications: Die casting finds application in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and more, owing to its ability to produce components with varying shapes, sizes, and functionalities.
Navigating the Landscape: Applications of Die Cast Metal Construction
Die cast metal components are ubiquitous in our daily lives, contributing to the functionality and aesthetics of various products. Some prominent applications include:
-
Automotive Industry: Die casting plays a crucial role in automotive manufacturing, producing components such as engine blocks, transmission housings, suspension parts, and body panels.
-
Electronics Industry: Die cast metal components are essential for electronic devices, serving as housings for smartphones, laptops, and other consumer electronics.
-
Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry relies heavily on die casting for the production of lightweight and durable components, such as aircraft parts and engine components.
-
Consumer Goods Industry: Die casting finds widespread use in the consumer goods industry, producing components for appliances, furniture, and other everyday items.
-
Medical Industry: The medical industry utilizes die cast metal components for medical devices, instruments, and implants, where strength, precision, and biocompatibility are critical.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Die Casting Techniques
The evolution of die casting has led to the development of advanced techniques that further enhance its capabilities and expand its application range:
-
Low-Pressure Die Casting: This technique uses lower injection pressures, making it suitable for casting more complex shapes and larger components.
-
Semi-Solid Die Casting: This process involves injecting a semi-solid metal slurry into the die, allowing for greater control over the microstructure and properties of the cast component.
-
Thixomolding: Similar to semi-solid die casting, this technique uses a thixotropic metal alloy that exhibits both solid and liquid properties, enabling the production of complex shapes with improved mechanical properties.
-
High-Pressure Die Casting: This technique utilizes extremely high injection pressures, allowing for the production of components with exceptionally thin walls and intricate details.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Die Cast Metal Construction
The future of die casting is bright, with ongoing advancements in materials, processes, and automation driving further innovation. Some key trends shaping the industry include:
-
Lightweight Materials: The increasing focus on fuel efficiency and environmental sustainability is driving the development of lighter, stronger alloys for die casting, enabling the production of components with reduced weight and improved performance.
-
Additive Manufacturing Integration: The integration of additive manufacturing (3D printing) with die casting offers new possibilities for creating complex geometries and incorporating customized features into cast components.
-
Advanced Automation: The adoption of advanced automation technologies, such as robotics and artificial intelligence, is streamlining die casting processes, enhancing productivity, and improving product quality.
-
Sustainability Focus: The industry is increasingly focused on sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient processes, and responsible disposal of waste.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns about Die Cast Metal Construction
Q: What are the limitations of die casting?
A: While die casting offers numerous advantages, it does have some limitations. The initial setup costs for die construction can be high, particularly for complex designs. Additionally, the process may not be suitable for casting very large components or those with extremely thin walls.
Q: What are the different types of die casting?
A: There are two main types of die casting: hot-chamber die casting and cold-chamber die casting. In hot-chamber die casting, the molten metal is held in a reservoir within the casting machine, while in cold-chamber die casting, the metal is poured into a shot sleeve before injection.
Q: What are the common alloys used in die casting?
A: Common alloys used in die casting include aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper, and tin. The choice of alloy depends on the specific application and required properties, such as strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
Q: How can I ensure the quality of die cast components?
A: Quality control is crucial in die casting. This involves careful inspection of the dies, monitoring of the casting process, and rigorous testing of the finished components to ensure they meet the required specifications.
Tips for Successful Die Cast Metal Construction
-
Choose the Right Alloy: Select an alloy that meets the specific requirements of the application, considering factors such as strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
-
Optimize Die Design: Ensure the die design is optimized for efficient filling, minimal distortion, and ease of ejection.
-
Control Process Parameters: Maintain tight control over process parameters, such as injection pressure, temperature, and cooling rate, to ensure consistent component quality.
-
Implement Quality Control Measures: Implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the process to identify and address any potential defects.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Strength and Innovation
Die cast metal construction has proven its enduring value across a wide range of industries, delivering components with exceptional strength, durability, and detail. As technology continues to advance, die casting is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of manufacturing, driving innovation and efficiency in the production of essential components for a wide array of applications. By understanding the fundamentals of die casting, its advantages, and its evolving landscape, manufacturers can leverage this powerful technology to create high-quality, reliable, and cost-effective components for a wide range of applications.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Strength of Die Cast Metal Construction: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
